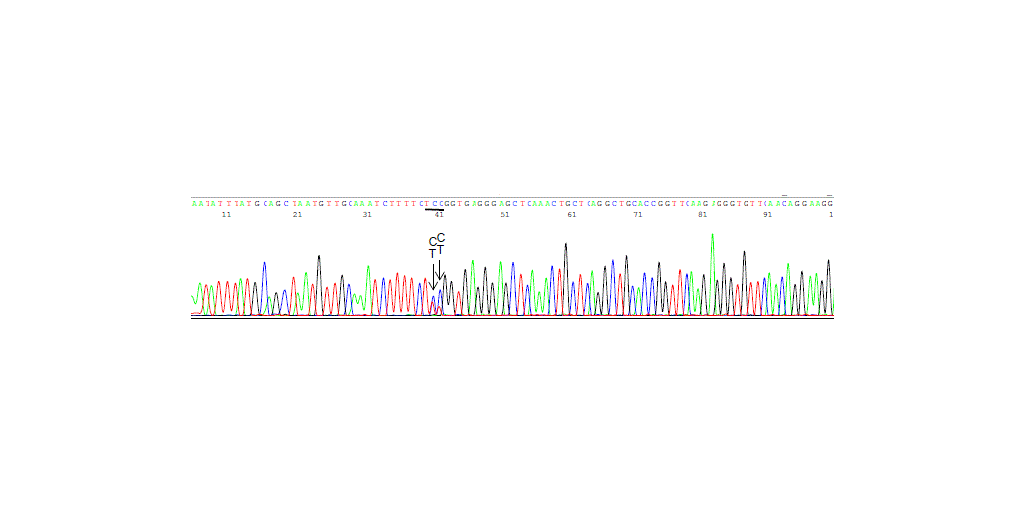
MILFORD, Conn.–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Sin Hang Lee, M.D., director of Milford Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory in Milford, Conn., announces that the Borrelia burgdorferi spirochetes invading the blood stream of the patients at the early localized stage of Lyme disease have duplicate flaB gene paralogs in their chromosome. For Sanger sequencing-based diagnosis of Lyme disease spirochetemia, the flaB gene with its paralogs is a more sensitive chromosomal target than the 16S rRNA gene aiming to detect a single Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium in venous blood specimens, as reported in an article published in Frontier in Bioscience-Scholar https://www.imrpress.com/journal/FBS/17/2/10.31083/FBS31280/htm
The article emphasizes the importance of timely differential centrifugation of the whole blood specimens to isolate the platelet fraction, which contains the spirochetes, for DNA extraction because delayed centrifugation allows the highly mobile spirochetes to attach to and invade the lymphocytes in the test tube at ambient temperature, then to be lost in the buffy coat. These findings are based on a study of the platelet-rich plasma specimens from 145 people, including 98 symptomatic patients, residing in Lyme disease-endemic areas in the United States during a Lyme disease season in 2023.
Based on the findings of this study, Dr. Lee has sent an open letter to the director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention urging the CDC to assist the hospital laboratories located in Lyme-disease endemic areas to implement methods to detect spirochetemia for early diagnosis and timely treatment of Borrelia burgdorferi infections http://www.dnalymetest.com/images/Urges_CDC_to_implement_Sanger_sequencing_for_Lyme_disease_diagnosis.pdf
Milford Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory is CLIA-certified. Its “nested PCR and direct automated DNA sequencing-based method for qualitative detection/identification of Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease) and Borrelia miyamotoi in whole blood specimens” is also approved by the New York State Department of Health for residents of the State of New York, said Dr. Lee.
Healthcare providers and laboratories interested in DNA sequencing-based diagnosis of Lyme disease spirochetemia for their patients may obtain more information by contacting Milford Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory via http://www.dnalymetest.com/contactus.html
Contacts
Wilda Garayua
Email: milfordmdx@dnalymetest.com